Health
Sodium Diacetate Health Effects
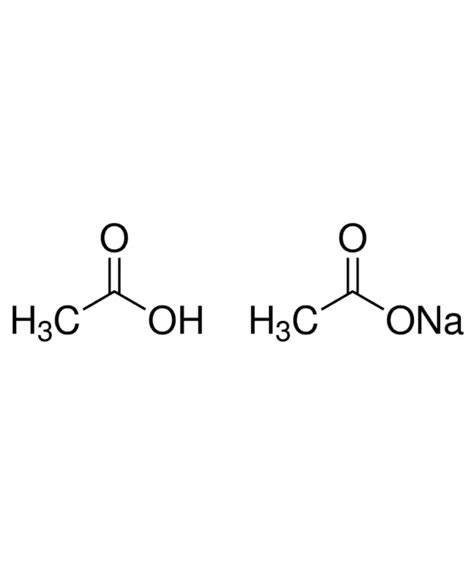
Introduction to Sodium Diacetate

Sodium diacetate is a synthetic preservative commonly used in food products to extend shelf life and enhance flavor. It is the sodium salt of acetic acid and is typically used in combination with other preservatives to prevent the growth of bacteria, mold, and yeast. Sodium diacetate is widely used in various food industries, including meat, poultry, and bakery products. However, its use has raised concerns about potential health effects, which will be discussed in this article.
Chemical Properties and Uses

Sodium diacetate is a white, crystalline powder with a characteristic vinegar-like odor. It is highly soluble in water and has a pH range of 5.5-7.5. The chemical formula for sodium diacetate is C4H7NaO4, and it is also known as sodium acetate, acetic acid, sodium salt. Sodium diacetate is used as a preservative, flavor enhancer, and pH regulator in various food products, including: * Meat and poultry products, such as sausages and bacon * Bakery products, such as bread and pastries * Snack foods, such as chips and popcorn * Condiments, such as ketchup and mayonnaise
Health Effects of Sodium Diacetate

The health effects of sodium diacetate have been extensively studied, and the results are summarized below: * Toxicity: Sodium diacetate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory agencies, such as the US FDA. However, high doses of sodium diacetate have been shown to cause toxicity in animal studies, including liver and kidney damage. * Allergic reactions: Some individuals may be allergic to sodium diacetate, which can cause symptoms such as hives, itching, and difficulty breathing. * Digestive issues: Sodium diacetate can cause digestive issues, such as diarrhea, stomach cramps, and nausea, in some individuals. * Cancer risk: Some studies have suggested a potential link between sodium diacetate and cancer, although the evidence is limited and inconclusive.
Regulatory Status

Sodium diacetate is regulated by various agencies worldwide, including: * US FDA: Sodium diacetate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the US FDA for use in food products. * European Food Safety Authority (EFSA): The EFSA has established an acceptable daily intake (ADI) of 0-30 mg/kg body weight per day for sodium diacetate. * World Health Organization (WHO): The WHO has established an ADI of 0-30 mg/kg body weight per day for sodium diacetate.
Alternatives to Sodium Diacetate

For individuals who are concerned about the potential health effects of sodium diacetate, there are several alternatives available: * Natural preservatives: Natural preservatives, such as vitamin E and rosemary extract, can be used to extend shelf life and enhance flavor. * Organic products: Organic products, which are free from synthetic preservatives, can be a healthier alternative. * Fresh products: Fresh products, which are free from preservatives, can be a healthier alternative.
👨⚕️ Note: It is essential to read food labels carefully and choose products that are low in sodium diacetate or use natural preservatives.
Conclusion and Recommendations

In conclusion, while sodium diacetate is generally recognized as safe, it is essential to be aware of the potential health effects and take steps to minimize exposure. Individuals who are concerned about the health effects of sodium diacetate can choose alternatives, such as natural preservatives, organic products, and fresh products. Additionally, regulatory agencies should continue to monitor the safety of sodium diacetate and update guidelines as necessary.
What is sodium diacetate?

+
Sodium diacetate is a synthetic preservative commonly used in food products to extend shelf life and enhance flavor.
Is sodium diacetate safe to consume?
+
Sodium diacetate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory agencies, but high doses can cause toxicity and allergic reactions in some individuals.
What are the alternatives to sodium diacetate?

+
Alternatives to sodium diacetate include natural preservatives, organic products, and fresh products.
Related Terms:
- sodium diacetate and sorbic acid



