US Soldier Salary Facts
Introduction to US Soldier Salary
The salary of a US soldier is a topic of interest for many, especially for those considering a career in the military. The compensation for US soldiers is designed to reflect their dedication, hard work, and the sacrifices they make for their country. It’s essential to understand that the salary structure for US soldiers is complex and can vary significantly based on several factors, including rank, time in service, and job specialty. In this article, we will delve into the details of US soldier salaries, exploring the various components that make up their total compensation package.
Basic Pay Scale

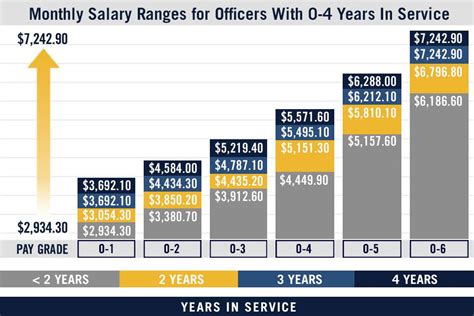
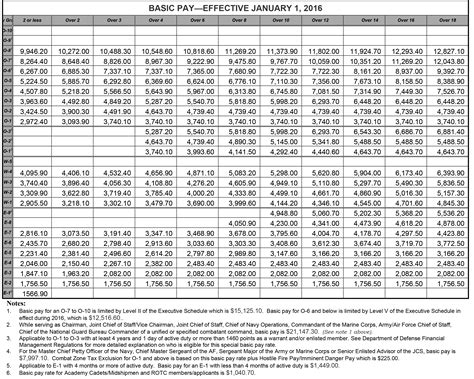
The basic pay scale for US soldiers is the foundation of their compensation. It is determined by their rank and the number of years they have served. The US military uses a pay grade system, which categorizes soldiers into different pay grades based on their rank. For example, an enlisted soldier entering the military as a Private (E-1) will start at a lower pay grade than a soldier who enters as an Officer. The basic pay scale is adjusted annually to reflect cost-of-living increases. The pay scale also varies between the different branches of the military, including the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard, although the differences are minor.
Allowances and Special Pays
In addition to basic pay, US soldiers can receive various allowances and special pays. These can include: - Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): This allowance is designed to offset the cost of housing for soldiers who do not live in military barracks. The amount varies based on the soldier’s location, rank, and whether they have dependents. - Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS): This allowance is meant to help cover the cost of food. It is a fixed rate for all soldiers and is not dependent on rank or location. - Special Duty Pay: Soldiers in certain specialties or who take on additional responsibilities can receive special duty pay. This can include hazardous duty pay, flight pay, or special duty assignment pay. - Deployment Pay: Soldiers who are deployed to certain areas may receive additional pay, including hazardous duty pay or imminent danger pay.
Benefits and Bonuses
US soldiers also receive a range of benefits and bonuses as part of their compensation package. These can include: - Health Insurance: Active-duty soldiers and their families are eligible for TRICARE, a comprehensive health insurance program. - Education Benefits: The military offers several education benefits, including the GI Bill, which can help pay for college or vocational training. - Retirement Benefits: Soldiers who serve for 20 years or more can retire and receive a pension, known as a retirement annuity. - Bonuses: Some soldiers may be eligible for bonuses, such as enlistment bonuses for joining the military, reenlistment bonuses for extending their service, or special skill bonuses for acquiring certain skills.
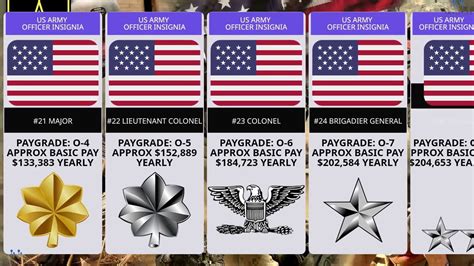
Factors Affecting Salary

Several factors can affect a US soldier’s salary, including: - Rank: Higher ranks receive higher basic pay and may be eligible for more allowances and special pays. - Time in Service: The longer a soldier serves, the higher their basic pay and the more benefits they may be eligible for. - Job Specialty: Certain job specialties, such as those in high-demand fields or requiring specialized skills, may receive higher pay or special pays. - Deployment: Soldiers who deploy to certain areas may receive additional pay, and those who serve in combat zones may be eligible for tax-free pay.
Salary Ranges
The salary range for US soldiers can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. Here is a rough estimate of what soldiers in different ranks and with different years of service might earn:
| Rank | Years of Service | Basic Pay |
|---|---|---|
| Private (E-1) | 2 years | Around 1,733 per month</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Sergeant (E-5)</td> <td>6 years</td> <td>Around 2,871 per month |
| Chief Warrant Officer 2 (W-2) | 10 years | Around 4,136 per month</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Colonel (O-6)</td> <td>20 years</td> <td>Around 8,786 per month |

👮 Note: These figures are approximate and do not include allowances, special pays, or bonuses, which can significantly increase the total compensation.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, the salary of a US soldier is a multifaceted compensation package that includes basic pay, allowances, special pays, benefits, and bonuses. Understanding these components is crucial for anyone considering a career in the military. The total compensation for US soldiers reflects their sacrifices, dedication, and the value they bring to the country. It’s a complex system designed to reward service, skills, and experience, ensuring that soldiers are well-compensated for their contributions.
How does the US military determine the basic pay for soldiers?

+
The basic pay for US soldiers is determined by their rank and the number of years they have served. The pay scale is adjusted annually to reflect cost-of-living increases.
What benefits do US soldiers receive in addition to their basic pay?

+
US soldiers receive a range of benefits, including health insurance, education benefits, retirement benefits, and access to on-base facilities. They may also receive allowances for housing and food, and special pays for certain duties or deployments.
How do deployments affect a US soldier’s salary?
+
Deployments can affect a US soldier’s salary in several ways. Soldiers deployed to certain areas may receive additional pay, such as hazardous duty pay or imminent danger pay. Deployments can also impact the eligibility for certain benefits and bonuses.
Related Terms:
- us army pay chart
- us soldier salary per month
- us army salaries by rank
- us military salary per month
- us army salary per month
- american soldier salary per month