7 Space Force Ranks

Introduction to Space Force Ranks

The United States Space Force (USSF) is the newest branch of the US military, established on December 20, 2019. As a separate branch, it has its own unique rank structure, which is similar to the US Air Force, but with some distinct differences. In this article, we will explore the different ranks within the Space Force, from the lowest to the highest, and provide an overview of the responsibilities and requirements associated with each rank.
Enlisted Ranks
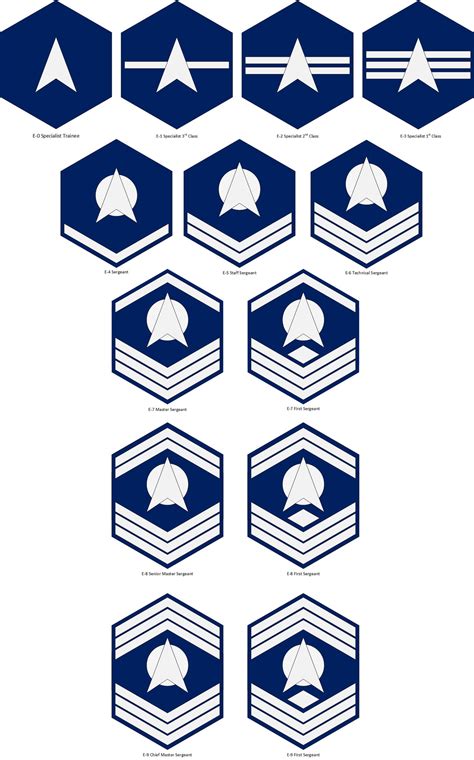
The enlisted ranks in the Space Force are divided into three categories: junior enlisted, non-commissioned officers (NCOs), and senior NCOs. Here are the enlisted ranks in the Space Force, in order from lowest to highest: * Spacecraft Systems Specialist 1st Class (E-1): The lowest enlisted rank in the Space Force, equivalent to an Airman Basic in the Air Force. * Spacecraft Systems Specialist 2nd Class (E-2): The second-lowest enlisted rank, equivalent to an Airman in the Air Force. * Spacecraft Systems Specialist 3rd Class (E-3): The third-lowest enlisted rank, equivalent to an Airman 1st Class in the Air Force. * Senior Spacecraft Systems Specialist (E-4): The first NCO rank, equivalent to a Senior Airman in the Air Force. * Staff Spacecraft Systems Specialist (E-5): The second NCO rank, equivalent to a Staff Sergeant in the Air Force. * Technical Spacecraft Systems Specialist (E-6): The third NCO rank, equivalent to a Technical Sergeant in the Air Force. * Master Spacecraft Systems Specialist (E-7): The fourth NCO rank, equivalent to a Master Sergeant in the Air Force. * Senior Master Spacecraft Systems Specialist (E-8): The fifth NCO rank, equivalent to a Senior Master Sergeant in the Air Force. * Chief Spacecraft Systems Specialist (E-9): The highest enlisted rank, equivalent to a Chief Master Sergeant in the Air Force.
Officer Ranks

The officer ranks in the Space Force are divided into two categories: company grade officers and field grade officers. Here are the officer ranks in the Space Force, in order from lowest to highest: * Second Lieutenant (O-1): The lowest officer rank, equivalent to a Second Lieutenant in the Air Force. * First Lieutenant (O-2): The second-lowest officer rank, equivalent to a First Lieutenant in the Air Force. * Captain (O-3): The third-lowest officer rank, equivalent to a Captain in the Air Force. * Major (O-4): The first field grade officer rank, equivalent to a Major in the Air Force. * Lieutenant Colonel (O-5): The second field grade officer rank, equivalent to a Lieutenant Colonel in the Air Force. * Colonel (O-6): The third field grade officer rank, equivalent to a Colonel in the Air Force. * Brigadier General (O-7): The first general officer rank, equivalent to a Brigadier General in the Air Force. * Major General (O-8): The second general officer rank, equivalent to a Major General in the Air Force. * Lieutenant General (O-9): The third general officer rank, equivalent to a Lieutenant General in the Air Force. * General (O-10): The highest officer rank, equivalent to a General in the Air Force.
Warrant Officer Ranks

The warrant officer ranks in the Space Force are specialized technical experts who provide advice and guidance to commanders. Here are the warrant officer ranks in the Space Force, in order from lowest to highest: * Warrant Officer 1 (W-1): The lowest warrant officer rank, equivalent to a Warrant Officer 1 in the Air Force. * Chief Warrant Officer 2 (W-2): The second-lowest warrant officer rank, equivalent to a Chief Warrant Officer 2 in the Air Force. * Chief Warrant Officer 3 (W-3): The third-lowest warrant officer rank, equivalent to a Chief Warrant Officer 3 in the Air Force. * Chief Warrant Officer 4 (W-4): The fourth-lowest warrant officer rank, equivalent to a Chief Warrant Officer 4 in the Air Force. * Chief Warrant Officer 5 (W-5): The highest warrant officer rank, equivalent to a Chief Warrant Officer 5 in the Air Force.
Rank Insignia

The rank insignia for the Space Force are similar to those used by the Air Force, but with some distinct differences. The enlisted ranks use a combination of chevrons and rocksers, while the officer ranks use a combination of bars and stars. The warrant officer ranks use a combination of bars and insignia.
| Rank | Insignia |
|---|---|
| Spacecraft Systems Specialist 1st Class (E-1) | No insignia |
| Spacecraft Systems Specialist 2nd Class (E-2) | One chevron |
| Spacecraft Systems Specialist 3rd Class (E-3) | Two chevrons |
| Senior Spacecraft Systems Specialist (E-4) | Three chevrons |
| Staff Spacecraft Systems Specialist (E-5) | Four chevrons |
| Technical Spacecraft Systems Specialist (E-6) | Five chevrons |
| Master Spacecraft Systems Specialist (E-7) | Six chevrons |
| Senior Master Spacecraft Systems Specialist (E-8) | Seven chevrons |
| Chief Spacecraft Systems Specialist (E-9) | Eight chevrons |
| Second Lieutenant (O-1) | One bar |
| First Lieutenant (O-2) | One bar with a star |
| Captain (O-3) | Two bars |
| Major (O-4) | One leaf |
| Lieutenant Colonel (O-5) | One leaf with a star |
| Colonel (O-6) | One eagle |
| Brigadier General (O-7) | One star |
| Major General (O-8) | Two stars |
| Lieutenant General (O-9) | Three stars |
| General (O-10) | Four stars |

💡 Note: The rank insignia for the Space Force are subject to change as the branch continues to develop and mature.
In summary, the Space Force has a unique rank structure that is similar to the Air Force, but with some distinct differences. The enlisted ranks are divided into junior enlisted, NCOs, and senior NCOs, while the officer ranks are divided into company grade officers and field grade officers. The warrant officer ranks are specialized technical experts who provide advice and guidance to commanders. Understanding the different ranks and their responsibilities is essential for anyone interested in joining the Space Force or working with the branch. The rank insignia for the Space Force are an important part of the branch’s identity and are used to distinguish between different ranks and specialties.
To recap, the key points of the Space Force ranks include the different categories of enlisted and officer ranks, the various responsibilities and requirements associated with each rank, and the unique rank insignia used by the branch. By understanding these key points, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the structure and organization of the Space Force. The Space Force is a rapidly evolving branch, and its rank structure is likely to continue to develop and mature in the coming years. As the branch continues to grow and expand, it is essential to stay up-to-date on the latest developments and changes to the rank structure.
In final thoughts, the Space Force ranks are an essential part of the branch’s identity and organization. By understanding the different ranks and their responsibilities, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the branch and its mission. The Space Force is a vital part of the US military, and its unique rank structure reflects its specialized role and responsibilities. As the branch continues to evolve and mature, it is essential to stay informed about the latest developments and changes to the rank structure.
What is the highest enlisted rank in the Space Force?

+
The highest enlisted rank in the Space Force is Chief Spacecraft Systems Specialist (E-9), which is equivalent to a Chief Master Sergeant in the Air Force.
What is the lowest officer rank in the Space Force?

+
The lowest officer rank in the Space Force is Second Lieutenant (O-1), which is equivalent to a Second Lieutenant in the Air Force.
What is the difference between a Space Force officer and an Air Force officer?

+
The main difference between a Space Force officer and an Air Force officer is the branch they serve in and the specific responsibilities and specialties associated with each branch. Space Force officers are trained to operate and maintain space systems, while Air Force officers are trained to operate and maintain aircraft and other aerial systems.
How do I join the Space Force?

+
To join the Space Force, you must meet the basic eligibility requirements, which include being a US citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 39, and meeting certain education and physical fitness standards. You can then apply to join the Space Force through the US Air Force website or by visiting a local recruiter.
What are the benefits of joining the Space Force?

+
The benefits of joining the Space Force include competitive pay and benefits, opportunities for education and training, and the chance to serve in a unique and specialized branch of the US military. Space Force members also have access to advanced technology and equipment, and are part of a rapidly evolving and growing branch.
Related Terms:
- space force rankings and pay
- space force enlisted rank chart
- space force rank abbreviation
- space force officer rank abbreviations
- space force officer grades
- highest ranking space force officer