Speed of Light in Mach

Introduction to the Speed of Light in Mach
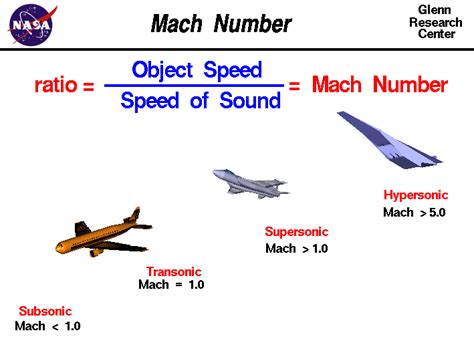
The speed of light is a fundamental constant in physics, representing the maximum speed at which all massless particles and waves, including light, can travel in a vacuum. This speed is approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (or about 186,282 miles per second). When discussing speeds, especially in the context of aerospace and aviation, the term “Mach” is often used. Mach numbers are a measure of the speed of an object relative to the speed of sound in the surrounding medium, usually air. In this context, the question arises: what is the speed of light in Mach?
Understanding Mach Numbers

To understand the speed of light in Mach, we first need to grasp what Mach numbers represent. The Mach number is named after Ernst Mach, an Austrian physicist and philosopher. It is defined as the ratio of the speed of an object to the speed of sound in the fluid (most commonly air) through which the object is moving. For example, an object traveling at Mach 1 is moving at the speed of sound, approximately 768 miles per hour (mph) or 1,236 kilometers per hour (km/h) at sea level in dry air at a temperature of 15 degrees Celsius.
Calculating the Speed of Light in Mach
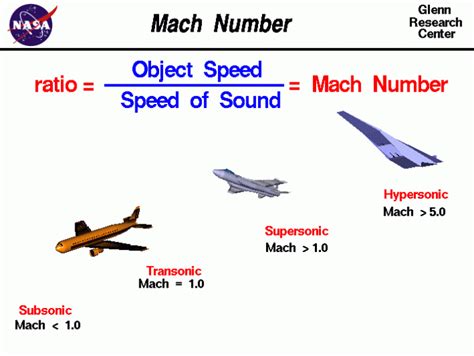
Given that the speed of sound in air at sea level and room temperature is about 343 meters per second (m/s), and the speed of light is approximately 299,792,458 m/s, we can calculate the Mach number of light. The formula for the Mach number is Mach = v / c, where v is the velocity of the object, and c is the speed of sound. However, in the context of comparing the speed of light to the speed of sound, we actually calculate it as Mach = c / v_sound, where c is the speed of light and v_sound is the speed of sound.
Using the given values: - Speed of light, c = 299,792,458 m/s - Speed of sound, v_sound = 343 m/s
The calculation would be: Mach = 299,792,458 m/s / 343 m/s ≈ 873,000
This result indicates that the speed of light is approximately 873,000 Mach, although this is a theoretical calculation and not a practical speed used in aviation or aerospace due to the vastly different scales and contexts in which these speeds apply.
Practical Applications and Considerations

The concept of the speed of light in Mach is more of a theoretical curiosity than a practical measure used in everyday applications. In aviation and aerospace, Mach numbers are crucial for understanding the performance and limitations of vehicles, particularly as they approach or exceed the speed of sound. However, the speed of light is so vastly greater than any achievable speed by man-made objects that it exists outside the realm of conventional aerospace engineering considerations.
🚀 Note: The speed of light, while fascinating to calculate in terms of Mach, does not directly influence the design or operation of aircraft or spacecraft in the way that subsonic, supersonic, or hypersonic speeds do.
Future of Speed and Aerospace Engineering
As humanity pushes the boundaries of speed and explores space, understanding the limits imposed by the laws of physics, including the speed of light, becomes increasingly important. While achieving a significant fraction of the speed of light is still in the realm of science fiction for macroscopic objects, advances in materials science, propulsion systems, and our understanding of space-time could potentially lead to breakthroughs that make faster-than-currently-possible travel more feasible.
In the meantime, the calculation of the speed of light in Mach serves as a reminder of the awe-inspiring scales involved in physics and the challenges that must be overcome to achieve significant fractions of the speed of light for practical space travel.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In summary, the speed of light, when calculated in terms of Mach, is an enormous number that highlights the fundamental differences between the speeds achievable by human-made objects and the universal speed limit set by the speed of light. This disparity underscores the significant technological and scientific hurdles that must be cleared to make rapid interstellar travel a reality. As we continue to explore and understand the universe, the interplay between the theoretical limits of speed and the practical capabilities of our technology will remain a fascinating and complex area of study and innovation.
What is the speed of light in a vacuum?
+
The speed of light in a vacuum is approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (or about 186,282 miles per second).
How is the Mach number calculated?

+
The Mach number is calculated as the ratio of the speed of an object to the speed of sound in the surrounding medium. For the speed of light in Mach, it’s calculated as the speed of light divided by the speed of sound.
What is the significance of the speed of light in Mach?

+
The significance lies in highlighting the vast difference between achievable speeds by human-made objects and the speed of light, emphasizing the challenges in achieving significant fractions of the speed of light for practical space travel.
Related Terms:
- Speed of sound in Mach
- Speed of light in mph
- How fast is Mach 100000000000000
- mach to light years
- mach to speed calculator
- lightspeed to mach