5 US Military Intel Jobs

Introduction to US Military Intel Jobs

The US military is one of the most advanced and complex organizations in the world, requiring a wide range of skills and expertise to maintain its operations and protect national security. One of the key components of the US military is its intelligence corps, which is responsible for gathering, analyzing, and disseminating critical information to support military operations and decision-making. In this blog post, we will explore five US military intel jobs that play a crucial role in supporting national security and military operations.
1. Intelligence Analyst

Intelligence analysts are responsible for analyzing and interpreting complex data and information to identify patterns, trends, and potential threats. They use their analytical skills to evaluate intelligence reports, identify gaps in knowledge, and provide recommendations to support military operations and decision-making. Intelligence analysts may specialize in specific areas, such as counterterrorism, cybersecurity, or geospatial intelligence. They work closely with other intelligence professionals, including collectors, analysts, and operators, to provide comprehensive intelligence support to military commanders and policymakers.
2. Cryptologic Linguist

Cryptologic linguists are responsible for analyzing and interpreting foreign language communications to identify potential threats and support military operations. They use their language skills to translate and transcribe foreign language communications, and then analyze the content to identify patterns, trends, and potential threats. Cryptologic linguists may specialize in specific languages, such as Arabic, Chinese, or Russian, and work closely with other intelligence professionals to provide comprehensive intelligence support to military commanders and policymakers.
3. Geospatial Intelligence Analyst

Geospatial intelligence analysts are responsible for analyzing and interpreting geospatial data, such as satellite imagery and map data, to identify patterns, trends, and potential threats. They use their analytical skills to evaluate geospatial data, identify gaps in knowledge, and provide recommendations to support military operations and decision-making. Geospatial intelligence analysts may specialize in specific areas, such as terrain analysis or urban planning, and work closely with other intelligence professionals to provide comprehensive intelligence support to military commanders and policymakers.
4. Human Intelligence Collector
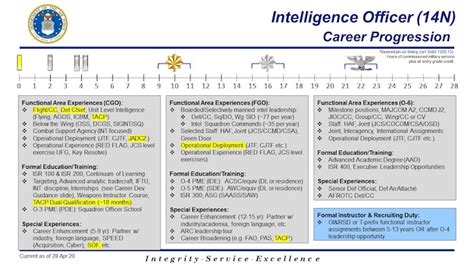
Human intelligence collectors are responsible for collecting and analyzing human intelligence, such as interrogations and surveillance, to identify potential threats and support military operations. They use their interpersonal skills to build relationships with sources, collect information, and analyze the content to identify patterns, trends, and potential threats. Human intelligence collectors may specialize in specific areas, such as counterintelligence or counterterrorism, and work closely with other intelligence professionals to provide comprehensive intelligence support to military commanders and policymakers.
5. Signals Intelligence Analyst

Signals intelligence analysts are responsible for analyzing and interpreting signals intelligence, such as communications intercepts and radar data, to identify potential threats and support military operations. They use their analytical skills to evaluate signals intelligence, identify gaps in knowledge, and provide recommendations to support military operations and decision-making. Signals intelligence analysts may specialize in specific areas, such as communications security or electronic warfare, and work closely with other intelligence professionals to provide comprehensive intelligence support to military commanders and policymakers.
📝 Note: These jobs require specialized training and clearance, and are typically available to US military personnel and civilians with security clearance.
To summarize, these five US military intel jobs play a crucial role in supporting national security and military operations. They require a range of skills and expertise, including analytical, language, and interpersonal skills, and involve working closely with other intelligence professionals to provide comprehensive intelligence support to military commanders and policymakers. By understanding the roles and responsibilities of these jobs, we can better appreciate the complexity and importance of the US military’s intelligence corps.
What is the role of an intelligence analyst in the US military?
+
Intelligence analysts are responsible for analyzing and interpreting complex data and information to identify patterns, trends, and potential threats, and providing recommendations to support military operations and decision-making.
What skills are required to be a cryptologic linguist in the US military?

+
Cryptologic linguists require language skills, analytical skills, and attention to detail, as well as the ability to work in a fast-paced and dynamic environment.
What is the difference between geospatial intelligence and signals intelligence?

+
Geospatial intelligence involves analyzing and interpreting geospatial data, such as satellite imagery and map data, while signals intelligence involves analyzing and interpreting signals intelligence, such as communications intercepts and radar data.
Related Terms:
- military intelligence job description
- 35 series jobs army
- counterintelligence jobs near me
- army intelligence civilian jobs
- military intelligence career path
- requirements to join military intelligence



