What is an Afterburner
Introduction to Afterburners

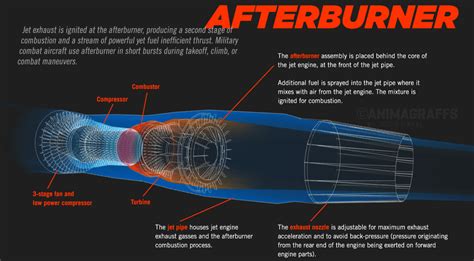
An afterburner is a component used in some jet engines to increase the thrust produced by the engine. It is typically used in military aircraft and some civilian jets to provide a temporary boost in power during critical phases of flight, such as takeoff, climb, or combat maneuvers. The afterburner works by injecting fuel into the hot exhaust gases produced by the engine and igniting it, which increases the temperature and velocity of the gases, resulting in a significant increase in thrust.
How Afterburners Work

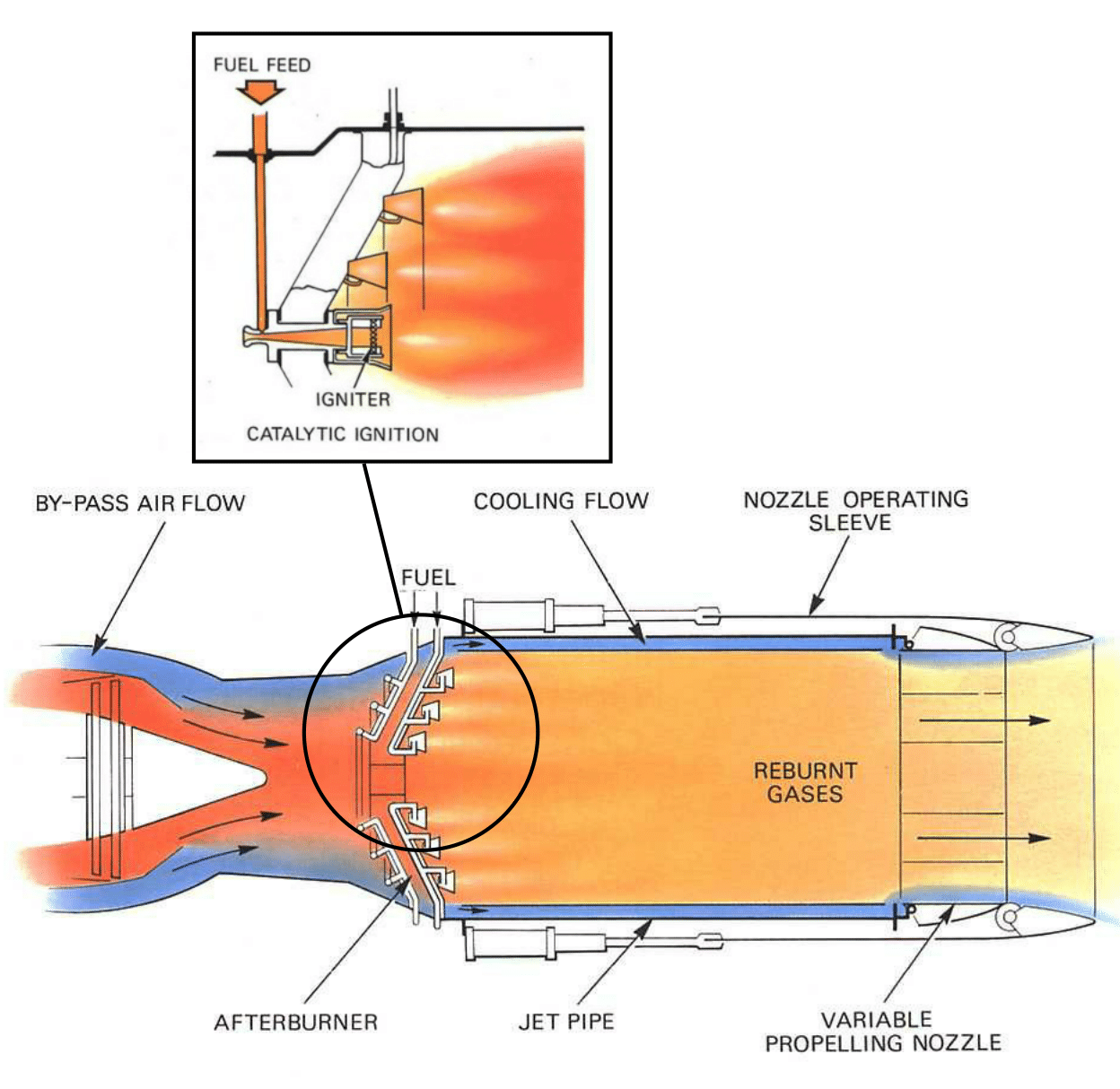
The afterburner is located at the rear of the engine, in the exhaust nozzle. When the afterburner is engaged, fuel is sprayed into the exhaust gases, which are then ignited by a spark plug or flame holder. This combustion process increases the temperature and pressure of the gases, which are then accelerated out of the back of the engine, producing a significant increase in thrust. The afterburner can increase the thrust of an engine by up to 50% or more, depending on the specific engine and afterburner design.
Types of Afterburners
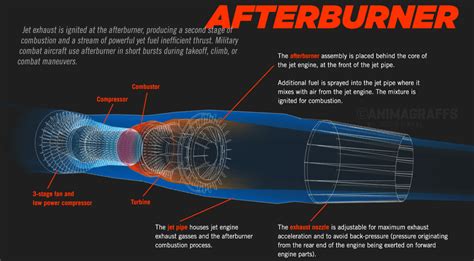
There are several types of afterburners, including: * Conventional afterburners: These are the most common type of afterburner and use a fuel spray nozzle to inject fuel into the exhaust gases. * Air-blast afterburners: These use a high-pressure air source to atomize the fuel and mix it with the exhaust gases. * Flame-holding afterburners: These use a flame holder to stabilize the flame and improve the combustion process. * Annular afterburners: These use a ring-shaped combustion chamber to increase the efficiency of the afterburner.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Afterburners

Afterburners have several advantages, including: * Increased thrust: Afterburners can provide a significant increase in thrust, which can be critical during certain phases of flight. * Improved acceleration: Afterburners can improve the acceleration of an aircraft, allowing it to climb faster and respond more quickly to threats. * Enhanced combat performance: Afterburners can provide a significant advantage in combat situations, allowing an aircraft to outmaneuver and outrun its opponents. However, afterburners also have several disadvantages, including: * Increased fuel consumption: Afterburners require a significant amount of fuel to operate, which can reduce the range and endurance of an aircraft. * Increased heat generation: Afterburners can generate a significant amount of heat, which can damage the engine and other components. * Increased maintenance requirements: Afterburners require regular maintenance to ensure they are functioning properly, which can be time-consuming and expensive.
💡 Note: Afterburners are typically used in military aircraft, but some civilian jets also use them to provide a temporary boost in power during critical phases of flight.
Applications of Afterburners

Afterburners are used in a variety of applications, including: * Military aircraft: Afterburners are used in many military aircraft, including fighters, bombers, and transport planes. * Civilian jets: Some civilian jets, such as business jets and private planes, use afterburners to provide a temporary boost in power during critical phases of flight. * Space exploration: Afterburners have been used in some spacecraft to provide a boost in power during launch and ascent.
| Engine Type | Afterburner Type | Thrust Increase |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional jet engine | Conventional afterburner | 20-30% |
| High-bypass jet engine | Air-blast afterburner | 30-40% |
| Turbofan engine | Flame-holding afterburner | 40-50% |
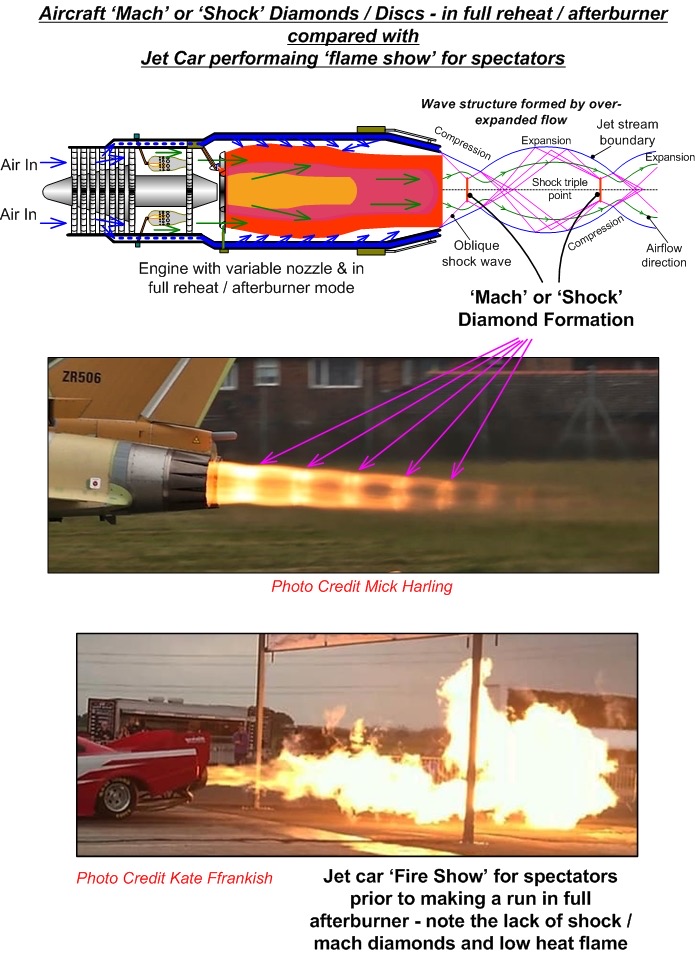
In summary, afterburners are a critical component of many jet engines, providing a temporary boost in power during critical phases of flight. While they have several advantages, including increased thrust and improved acceleration, they also have several disadvantages, including increased fuel consumption and heat generation. Afterburners are used in a variety of applications, including military aircraft, civilian jets, and space exploration.
To summarize the key points, afterburners are an essential part of many jet engines, and their use can significantly impact the performance of an aircraft. By understanding how afterburners work and their advantages and disadvantages, we can better appreciate the complexity and sophistication of modern jet engines. The use of afterburners will likely continue to play a critical role in the development of future aircraft, and their applications will continue to expand into new areas, such as space exploration.
What is the purpose of an afterburner?

+
The purpose of an afterburner is to increase the thrust produced by a jet engine, typically used in military aircraft and some civilian jets to provide a temporary boost in power during critical phases of flight.
How does an afterburner work?

+
An afterburner works by injecting fuel into the hot exhaust gases produced by the engine and igniting it, which increases the temperature and velocity of the gases, resulting in a significant increase in thrust.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of afterburners?
+
The advantages of afterburners include increased thrust, improved acceleration, and enhanced combat performance. The disadvantages include increased fuel consumption, increased heat generation, and increased maintenance requirements.
Related Terms:
- afterburner explained
- afterburner jet engine diagram
- afterburner vs augmentor
- when was the afterburner invented
- first jet with afterburner
- what does an afterburner do



