5 Military Branches

Introduction to the 5 Military Branches

The military is a vital institution in many countries, responsible for defending the nation and its interests. In the United States, there are five military branches, each with its unique mission, responsibilities, and culture. Understanding these branches is essential for anyone interested in joining the military or learning more about the country’s defense system. In this article, we will delve into the world of the five military branches, exploring their history, roles, and requirements.
The Five Military Branches

The five military branches are: * United States Army: The Army is the largest of the five branches, responsible for land-based military operations. Its primary mission is to protect the country and its interests by fighting and winning wars on land. * United States Navy: The Navy is responsible for sea-based military operations, protecting the country’s interests at sea, and maintaining the freedom of the seas. * United States Air Force: The Air Force is responsible for air-based military operations, protecting the country’s interests in the air, and maintaining air superiority. * United States Marine Corps: The Marine Corps is a branch of the Navy, responsible for ground combat operations, and is known for its elite fighting force. * United States Coast Guard: The Coast Guard is a unique branch that operates under the Department of Homeland Security during peacetime, but can be transferred to the Navy during wartime. Its primary mission is to protect the country’s coastlines and enforce maritime law.
History of the 5 Military Branches
The history of the five military branches dates back to the American Revolution, when the Continental Army was formed to fight against the British. Over time, the Army, Navy, and Marine Corps evolved, and the Air Force was established as a separate branch in 1947. The Coast Guard has its roots in the Revenue Cutter Service, which was established in 1790. Each branch has its unique history, traditions, and culture, shaped by its mission and responsibilities.
Roles and Responsibilities
Each branch has its specific roles and responsibilities: * The Army is responsible for land-based operations, including combat, peacekeeping, and humanitarian missions. * The Navy is responsible for sea-based operations, including combat, transportation, and humanitarian missions. * The Air Force is responsible for air-based operations, including combat, transportation, and reconnaissance missions. * The Marine Corps is responsible for ground combat operations, including amphibious assaults and expeditionary operations. * The Coast Guard is responsible for maritime law enforcement, search and rescue, and marine safety.
Requirements for Joining the Military

To join the military, individuals must meet certain requirements, including: * Being a U.S. citizen or permanent resident * Being between the ages of 17 and 35 (with some exceptions) * Meeting physical fitness standards * Passing the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test * Completing basic training
💡 Note: Each branch has its unique requirements, and some may have additional requirements or restrictions.
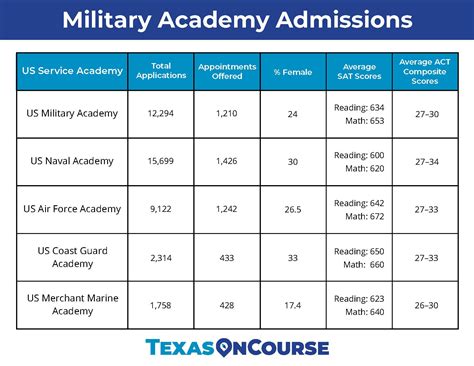
Comparison of the 5 Military Branches

Here is a comparison of the five military branches:
| Branch | Size | Mission | Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Army | 475,000 active duty | Land-based operations | High school diploma, ASVAB score |
| Navy | 330,000 active duty | Sea-based operations | High school diploma, ASVAB score |
| Air Force | 329,000 active duty | Air-based operations | High school diploma, ASVAB score |
| Marine Corps | 186,000 active duty | Ground combat operations | High school diploma, ASVAB score |
| Coast Guard | 42,000 active duty | Maritime law enforcement | High school diploma, ASVAB score |

In summary, the five military branches are unique institutions with different missions, roles, and requirements. Understanding these branches is essential for anyone interested in joining the military or learning more about the country’s defense system. By exploring the history, roles, and requirements of each branch, individuals can make informed decisions about their future and contribute to the country’s defense and security.
What are the five military branches?

+
The five military branches are the United States Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard.
What is the primary mission of the Army?

+
The primary mission of the Army is to protect the country and its interests by fighting and winning wars on land.
Can I join the military if I am not a U.S. citizen?

+
Yes, you can join the military if you are a permanent resident, but you must meet certain requirements and follow the naturalization process.
What is the ASVAB test?

+
The ASVAB test is the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery test, which measures an individual’s aptitude for various military careers.
How long is basic training?

+
Basic training, also known as boot camp, typically lasts 7-12 weeks, depending on the branch and individual circumstances.
Related Terms:
- best military branches to join
- easiest military branch
- army branch requirements



