5 Mental Health Differences

Introduction to Mental Health Differences

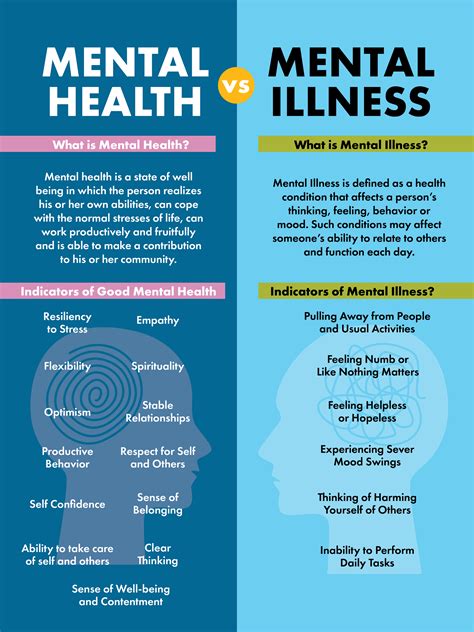
Mental health is a complex and multifaceted aspect of human well-being, and there are many differences in how individuals experience and manage their mental health. Understanding these differences is crucial for providing effective support and promoting overall wellness. In this article, we will explore five key mental health differences, including the impact of personality traits, coping mechanisms, social support, cultural background, and access to resources.
Personality Traits and Mental Health
Personality traits play a significant role in shaping an individual’s mental health. For example, introverted individuals may be more prone to anxiety and depression due to their tendency to internalize their emotions, while extroverted individuals may be more resilient to stress and adversity due to their ability to seek social support. Additionally, personality traits such as neuroticism and perfectionism can increase an individual’s risk of developing mental health conditions.
Some key points to consider when examining the relationship between personality traits and mental health include: * Emotional regulation: Individuals with certain personality traits, such as neuroticism, may struggle with regulating their emotions, leading to increased stress and anxiety. * Coping mechanisms: Personality traits can influence an individual’s choice of coping mechanisms, with some traits leading to more adaptive or maladaptive coping strategies. * Social support: Personality traits can also impact an individual’s ability to seek and maintain social support, which is essential for mental health and well-being.
Coping Mechanisms and Mental Health

Coping mechanisms are the strategies individuals use to manage stress, adversity, and other challenging situations. Effective coping mechanisms, such as problem-focused coping and emotional regulation, can help individuals maintain good mental health, while ineffective coping mechanisms, such as avoidance and substance use, can exacerbate mental health issues. It is essential to recognize that coping mechanisms can vary across individuals and situations, and no single approach is suitable for everyone.
Some key points to consider when examining coping mechanisms and mental health include: * Problem-focused coping: This involves actively addressing the source of stress or adversity, which can be an effective way to manage mental health. * Emotional regulation: This involves managing and regulating emotions, which can help individuals cope with stress and adversity. * Social support: Seeking social support from friends, family, or mental health professionals can be an essential coping mechanism for maintaining good mental health.
Social Support and Mental Health

Social support is a critical factor in maintaining good mental health. Strong social connections can provide individuals with a sense of belonging, emotional support, and practical assistance, which can help mitigate the effects of stress and adversity. Conversely, weak social connections or social isolation can increase an individual’s risk of developing mental health conditions.
Some key points to consider when examining the relationship between social support and mental health include: * Social networks: Individuals with strong social networks tend to have better mental health outcomes than those with weak social connections. * Emotional support: Social support can provide individuals with emotional support, which can help them cope with stress and adversity. * Practical assistance: Social support can also provide individuals with practical assistance, such as help with daily tasks or financial support.
Cultural Background and Mental Health
Cultural background can significantly impact an individual’s mental health. Cultural differences in values, beliefs, and practices can influence an individual’s perception of mental health, their willingness to seek help, and their choice of coping mechanisms. For example, collectivist cultures may prioritize family and community over individual needs, while individualist cultures may prioritize personal autonomy and self-reliance.
Some key points to consider when examining the relationship between cultural background and mental health include: * Cultural values: Cultural values can influence an individual’s perception of mental health and their willingness to seek help. * Cultural practices: Cultural practices, such as traditional healing practices, can also impact an individual’s mental health outcomes. * Language barriers: Language barriers can create challenges for individuals seeking mental health support, particularly in cultures where mental health services are not readily available.
Access to Resources and Mental Health

Access to resources, such as mental health services, education, and economic opportunities, can significantly impact an individual’s mental health. Limited access to resources can increase an individual’s risk of developing mental health conditions, while adequate access to resources can provide individuals with the support and tools they need to maintain good mental health.
Some key points to consider when examining the relationship between access to resources and mental health include: * Mental health services: Access to mental health services, such as therapy and counseling, can provide individuals with the support they need to manage their mental health. * Education: Education can provide individuals with the knowledge and skills they need to manage their mental health and make informed decisions about their well-being. * Economic opportunities: Economic opportunities, such as employment and financial stability, can provide individuals with a sense of security and stability, which can help mitigate the effects of stress and adversity.
📝 Note: It is essential to recognize that mental health differences are complex and multifaceted, and that no single approach is suitable for everyone. By understanding these differences, we can provide more effective support and promote overall wellness.
In summary, mental health differences are shaped by a complex interplay of factors, including personality traits, coping mechanisms, social support, cultural background, and access to resources. By recognizing and understanding these differences, we can provide more effective support and promote overall wellness. This understanding can help individuals, mental health professionals, and policymakers develop targeted interventions and strategies to address the unique needs of diverse populations and promote better mental health outcomes.
Related Terms:
- Behavioral health vs Psychiatry
- Psychological health vs mental health
- Behavioral health examples
- Mental and behavioral health
- Behavioral and mental health services
- Mental health and behaviour