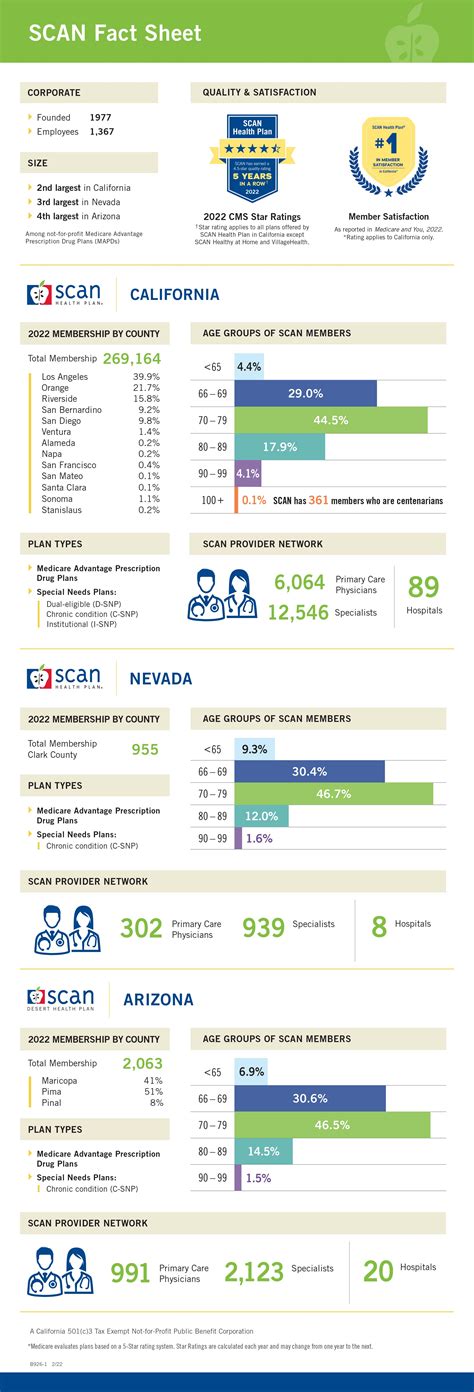
Big Three Collection Health Insurance
Introduction to the Big Three Collection Health Insurance

The Big Three Collection Health Insurance refers to the three primary types of health insurance coverage that individuals and families can purchase to protect themselves against medical expenses. These include Medicare, Medicaid, and Private Health Insurance. Understanding the differences and benefits of each type is crucial for making informed decisions about one’s health insurance needs. In this article, we will delve into the details of each type, exploring their eligibility criteria, coverage options, and the advantages of having health insurance.
Medicare: A Federal Health Insurance Program
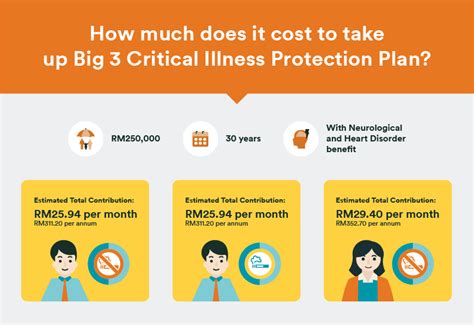
Medicare is a federal health insurance program designed primarily for individuals 65 or older, certain younger people with disabilities, and people with End-Stage Renal Disease (permanent kidney failure requiring dialysis or a transplant). It is divided into several parts, including: - Part A (Hospital Insurance): Covers inpatient hospital stays, skilled nursing facility care, hospice care, and some home health care. - Part B (Medical Insurance): Covers certain doctors’ services, outpatient care, medical supplies, and preventive services. - Part C (Medicare Advantage): A type of Medicare health plan offered by a private company that contracts with Medicare. - Part D (Prescription Drug Coverage): Offers prescription drug coverage.
Medicare is a vital resource for millions of Americans, providing access to necessary medical care. However, it may not cover all health care costs, and beneficiaries often need to purchase additional coverage to fill these gaps.
Medicaid: A Joint Federal and State Program

Medicaid is a joint federal and state program that provides health coverage to millions of Americans, including eligible low-income adults, children, pregnant women, elderly adults, and people with disabilities. The program varies from state to state, with each state determining its own eligibility criteria, services covered, and payment rates for healthcare providers. Medicaid covers a range of health services, including: - Doctor visits - Hospital stays - Prescription drugs - Vision and dental care for children - Long-term care
Medicaid plays a crucial role in ensuring that low-income individuals and families have access to essential health care services.
Private Health Insurance

Private health insurance is purchased by individuals or families directly from an insurance company. It can also be provided through an employer. Private insurance plans vary widely in terms of what they cover, how much they cost, and the requirements for eligibility. Key features of private health insurance include: - Network: Insurers contract with a network of healthcare providers to offer discounted services. - Deductible: The amount the insured must pay out-of-pocket before the insurance starts to pay. - Co-payments and Co-insurance: Fees for services after the deductible is met. - Maximum Out-of-Pocket: The maximum amount the insured pays for health care expenses in a year.
Private health insurance offers flexibility and often a wider range of provider choices compared to public insurance programs. However, it can be more expensive, and not everyone may be eligible or able to afford it.
Benefits of Health Insurance

Having health insurance, regardless of the type, offers numerous benefits, including: - Financial Protection: Against unexpected medical bills that could lead to financial ruin. - Access to Care: Ensures that individuals can receive necessary medical care without delay due to cost concerns. - Preventive Care: Many health insurance plans cover preventive services at no additional cost, promoting early detection and treatment of health issues. - Peace of Mind: Knowing that one has a financial safety net in case of medical emergencies can reduce stress and anxiety.
Choosing the Right Health Insurance

Selecting the appropriate health insurance plan involves considering several factors, such as: - Age and Health Status: Older individuals or those with pre-existing conditions may prioritize comprehensive coverage. - Income Level: Lower-income individuals may qualify for Medicaid or subsidized private insurance plans. - Employment Status: Those employed may have access to employer-sponsored health plans. - Family Size and Needs: Families with children may need to consider plans that cover pediatric care, including vision and dental services.
It’s essential to weigh these factors against the costs and benefits of each insurance type to make an informed decision.
Comparing the Big Three

| Type of Insurance | Eligibility | Coverage | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medicare | 65+, certain disabilities, ESRD | Hospital, medical, prescription drug | Varies by part, some free, some premium-based |
| Medicaid | Low-income adults, children, pregnant women, elderly, people with disabilities | Comprehensive, including long-term care | Generally free or low-cost to eligible individuals |
| Private Health Insurance | Varies, often employer-sponsored or individual purchase | Wide range of options, can include dental, vision | Can be expensive, premiums, deductibles, co-pays |
💡 Note: Understanding the specifics of each insurance type, including eligibility, coverage, and costs, is crucial for making informed decisions about health insurance.
In conclusion, the Big Three Collection Health Insurance—Medicare, Medicaid, and Private Health Insurance—offers a range of options for individuals and families to protect themselves against the financial risks associated with medical care. Each type of insurance has its unique characteristics, advantages, and eligibility criteria. By understanding these differences and considering personal circumstances, individuals can make informed decisions about their health insurance needs, ensuring they have access to necessary medical care without facing financial hardship.
What is the main difference between Medicare and Medicaid?

+
Medicare is primarily for individuals 65 or older, or those with certain disabilities, while Medicaid is for low-income adults, children, pregnant women, elderly adults, and people with disabilities.
Can I have both Medicare and Medicaid?

+
Yes, it is possible to be dual-eligible, meaning you qualify for both Medicare and Medicaid. This often provides comprehensive coverage with minimal out-of-pocket costs.
How do I choose the right private health insurance plan for me?

+
Consider your health needs, budget, and whether you have a preferred healthcare provider or network. Review the plan’s coverage, deductibles, co-pays, and maximum out-of-pocket costs to make an informed decision.
Related Terms:
- Big 3 Critical illness insurance
- Big 3 Critical Illness FWD
- Singlife Big 3 Critical illness
- 42 critical illness FWD
- Singlife Comprehensive Critical Illness review
- FWD health insurance