Global Health Rheumatology Matters
Introduction to Global Health Rheumatology

The field of rheumatology, which deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and management of disorders related to the joints, muscles, and bones, has become increasingly important in the context of global health. Rheumatic diseases affect millions of people worldwide, causing significant morbidity, mortality, and disability. The impact of these diseases is not limited to the individual but also has significant socioeconomic implications, affecting productivity, healthcare systems, and the overall quality of life. As the global population ages and the prevalence of rheumatic diseases increases, it is essential to prioritize rheumatology in global health discussions.
Prevalence and Impact of Rheumatic Diseases

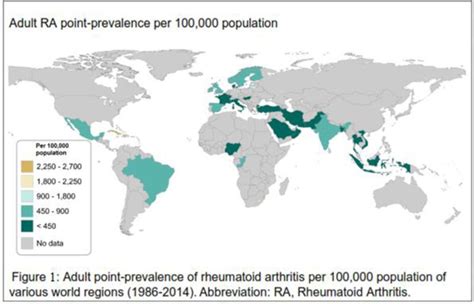
Rheumatic diseases encompass a wide range of conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, lupus, fibromyalgia, and gout, among others. These diseases can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or geographic location, although some are more prevalent in certain populations. For instance, rheumatoid arthritis is more common in women, while gout is more frequently seen in men. The prevalence of these diseases varies globally, with some regions having higher rates due to factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and access to healthcare.
Global Health Initiatives in Rheumatology

To address the growing burden of rheumatic diseases, various global health initiatives have been launched. These initiatives aim to improve awareness, diagnosis, treatment, and management of rheumatic diseases worldwide. One key strategy is the development of guidelines and protocols for the diagnosis and treatment of rheumatic diseases, tailored to different resource settings. This ensures that healthcare providers in low- and middle-income countries have access to evidence-based practices that can be adapted to their local contexts. Additionally, training programs for healthcare professionals are crucial, as they enhance the capacity of local healthcare systems to manage rheumatic diseases effectively.
Challenges in Global Health Rheumatology

Despite the progress made, several challenges hinder the effective management of rheumatic diseases globally. One of the significant challenges is the lack of access to healthcare services, particularly in rural and underserved areas. Many people with rheumatic diseases face barriers in accessing diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing care, leading to delayed diagnosis and poor outcomes. Another challenge is the shortage of rheumatology specialists in many parts of the world. This shortage exacerbates the existing healthcare gap, making it difficult for patients to receive specialized care. Socioeconomic factors, including poverty and lack of insurance, also play a critical role, as they can limit an individual’s ability to afford healthcare services and medications.
Role of Technology in Improving Access to Rheumatology Care

Technology has the potential to revolutionize the field of rheumatology, especially in improving access to care. Telemedicine platforms can connect patients with rheumatology specialists remotely, reducing the need for travel and increasing accessibility. Digital health tools and mobile apps can also facilitate self-management of rheumatic diseases, enabling patients to track their symptoms, adherence to medication, and lifestyle changes. Furthermore, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) can aid in the diagnosis and prediction of disease outcomes, potentially leading to more personalized and effective treatment strategies.
Future Directions in Global Health Rheumatology

The future of global health rheumatology is promising, with ongoing research and innovations aimed at improving our understanding and management of rheumatic diseases. Personalized medicine, which involves tailoring treatment to the individual based on their genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, is an area of significant interest. Additionally, preventive strategies focused on reducing the risk factors for rheumatic diseases, such as obesity and smoking, are being explored. International collaborations and global health partnerships will be essential in addressing the complex challenges posed by rheumatic diseases, ensuring that advances in rheumatology benefit all populations worldwide.
🌎 Note: Collaboration among healthcare professionals, researchers, policymakers, and patients is crucial for advancing the field of global health rheumatology and ensuring that rheumatic diseases are managed effectively and equitably across the globe.
As we move forward in addressing the challenges and opportunities in global health rheumatology, it is clear that a multifaceted approach is necessary. This includes not only advancing medical knowledge and practice but also addressing the socioeconomic and environmental determinants of health. By prioritizing rheumatology in global health discussions and actions, we can work towards a future where all individuals, regardless of their background or location, have access to the care and support they need to manage rheumatic diseases and lead fulfilling lives.
What are the most common rheumatic diseases globally?

+
The most common rheumatic diseases include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, fibromyalgia, and gout. These diseases vary in prevalence and impact across different regions and populations.
How does access to healthcare affect the management of rheumatic diseases?

+
Access to healthcare is crucial for the effective management of rheumatic diseases. Limited access can lead to delayed diagnosis, inadequate treatment, and poor outcomes. Initiatives to improve access to healthcare services, including telemedicine and community-based care, are essential for addressing these challenges.
What role can technology play in improving rheumatology care?
+
Technology, including telemedicine, digital health tools, and artificial intelligence, has the potential to revolutionize rheumatology care. It can improve access to specialists, enhance patient self-management, and aid in the diagnosis and treatment of rheumatic diseases, leading to more personalized and effective care.
Related Terms:
- Rheumatology PDF
- My rheumatology
- Rheumatology Foundation
- Rheumatology Congress
- Online rheumatology
- ARC Rheumatology



