Good Soil Health Index Matters

Introduction to Soil Health
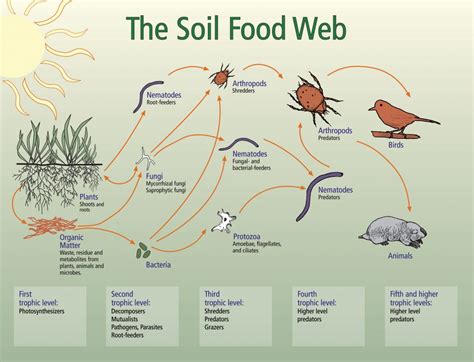
Soil health is a critical component of any ecosystem, playing a vital role in supporting plant growth, filtering water, and storing carbon. Soil health index is a measure used to assess the overall condition of the soil, taking into account various physical, chemical, and biological properties. A good soil health index matters for several reasons, including improved crop productivity, enhanced ecosystem services, and increased resilience to climate change. In this blog post, we will delve into the importance of soil health, the factors that influence it, and the benefits of maintaining a good soil health index.
Factors Influencing Soil Health
Several factors can influence soil health, including: * Soil type and structure: Different soil types have unique properties that affect their health, such as water-holding capacity, nutrient availability, and erosion resistance. * Climate and weather patterns: Climate and weather patterns can impact soil health by affecting temperature, moisture, and erosion rates. * Land use and management practices: Human activities such as farming, deforestation, and urbanization can significantly impact soil health by altering soil structure, reducing organic matter, and increasing erosion. * Soil biota and biodiversity: Soil biota, including microorganisms, insects, and other organisms, play a crucial role in maintaining soil health by decomposing organic matter, fixing nitrogen, and fighting plant diseases.
Benefits of Good Soil Health

Maintaining a good soil health index has numerous benefits, including: * Improved crop productivity: Healthy soils support plant growth, increase crop yields, and enhance food security. * Enhanced ecosystem services: Healthy soils provide ecosystem services such as water filtration, carbon sequestration, and habitat provision for biodiversity. * Increased resilience to climate change: Healthy soils can help mitigate the effects of climate change by storing carbon, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and supporting plant growth in extreme weather conditions. * Better water quality: Healthy soils can filter water, reducing sedimentation and nutrient pollution in waterways.
Assessing Soil Health

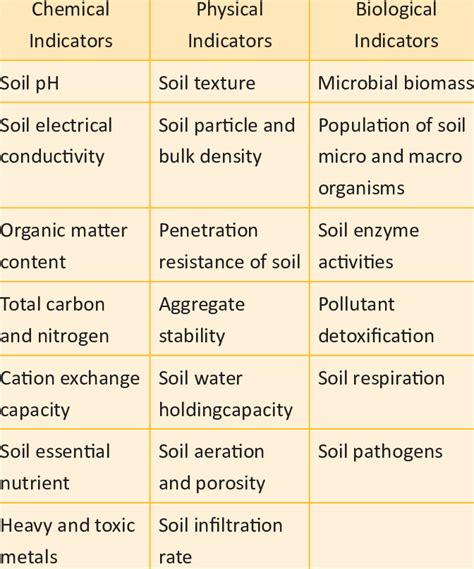
Assessing soil health involves evaluating various physical, chemical, and biological properties, including:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Soil texture | The proportion of sand, silt, and clay particles in the soil |
| Soil pH | The acidity or alkalinity of the soil |
| Organic matter content | The amount of carbon-based compounds in the soil |
| Microbial activity | The presence and activity of microorganisms in the soil |
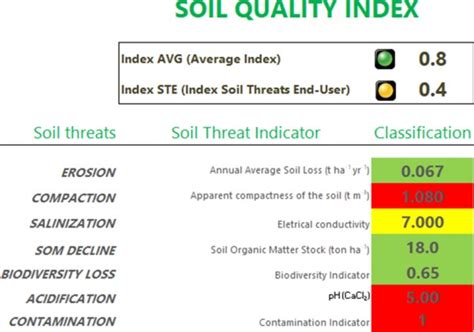
These properties can be assessed using various methods, including soil testing, field observations, and remote sensing technologies.
🌎 Note: Assessing soil health is a complex process that requires a comprehensive approach, taking into account various physical, chemical, and biological properties.
Maintaining Good Soil Health
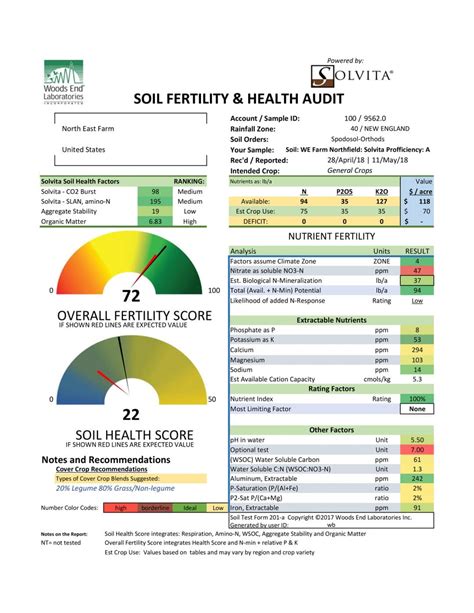
Maintaining good soil health requires a combination of conservation tillage, cover cropping, crop rotation, and integrated pest management. These practices can help: * Reduce soil erosion and degradation * Increase soil organic matter and biodiversity * Improve soil structure and water-holding capacity * Support plant growth and crop productivity
Challenges and Opportunities

Despite the importance of soil health, there are several challenges and opportunities that need to be addressed, including: * Climate change: Climate change can impact soil health by altering temperature, moisture, and erosion rates. * Land degradation: Land degradation can reduce soil health by altering soil structure, reducing organic matter, and increasing erosion. * Sustainable agriculture: Sustainable agriculture practices can help maintain good soil health by reducing tillage, increasing cover cropping, and promoting crop rotation.
In summary, maintaining a good soil health index is crucial for supporting ecosystem services, improving crop productivity, and mitigating the effects of climate change. By understanding the factors that influence soil health, assessing soil health, and implementing conservation practices, we can work towards maintaining healthy soils and supporting a sustainable future.
As we reflect on the importance of soil health, it becomes clear that maintaining a good soil health index is essential for supporting life on Earth. By taking a comprehensive approach to soil health, we can ensure that our soils continue to provide ecosystem services, support plant growth, and mitigate the effects of climate change. Ultimately, the health of our soils is intricately linked to our own well-being, and it is our responsibility to protect and preserve this vital resource for future generations.
What is soil health index?

+
Soil health index is a measure used to assess the overall condition of the soil, taking into account various physical, chemical, and biological properties.
Why is soil health important?

+
Soil health is important because it supports ecosystem services, improves crop productivity, and mitigates the effects of climate change.
How can I improve soil health?

+
You can improve soil health by implementing conservation practices such as reducing tillage, increasing cover cropping, and promoting crop rotation.
Related Terms:
- Soil health indicators PDF
- Chemical indicators of soil health
- Biological indicators of soil health
- Soil health article
- Soil health assessment
- Soil health FAO