Submarines Depth Explained
Introduction to Submarine Depth
Submarines are complex machines that operate underwater, and their ability to dive to great depths is one of their most fascinating features. The depth to which a submarine can dive is determined by a combination of factors, including its design, materials, and equipment. In this article, we will explore the concept of submarine depth, the factors that affect it, and the different types of submarines that exist.
Factors Affecting Submarine Depth
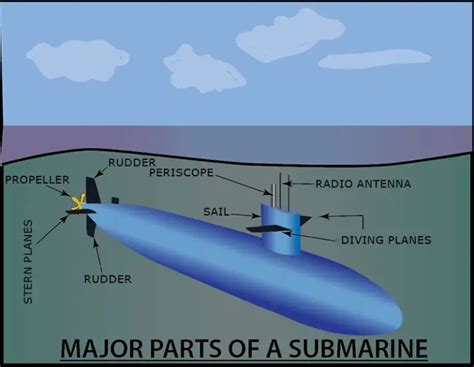
Several factors affect a submarine’s ability to dive to great depths. These include: * Hull design: The shape and structure of the submarine’s hull play a crucial role in determining its depth capability. A hull that is designed to withstand high pressures is essential for deep diving. * Materials: The materials used to build the submarine’s hull and other components must be able to withstand the crushing pressures of the deep ocean. * Ballast tanks: Submarines use ballast tanks to control their buoyancy and dive to different depths. The size and number of ballast tanks affect the submarine’s ability to dive deep. * Life support systems: The submarine’s life support systems, including its air supply and cooling systems, must be able to sustain the crew for extended periods at depth. * Pressure hull: The pressure hull is the strongest part of the submarine and is designed to withstand the external pressure of the water.
Types of Submarines
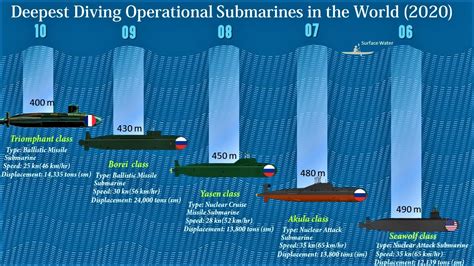
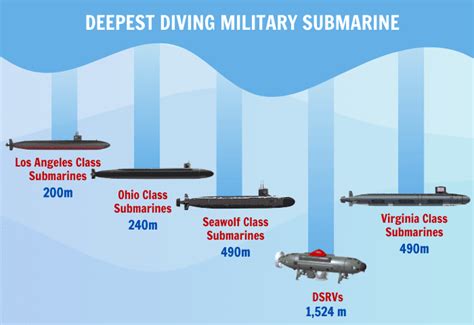
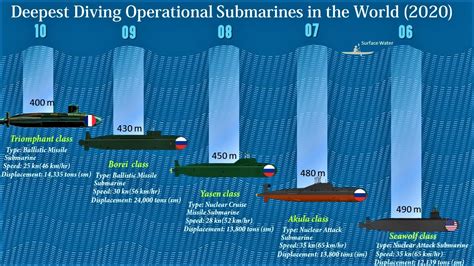
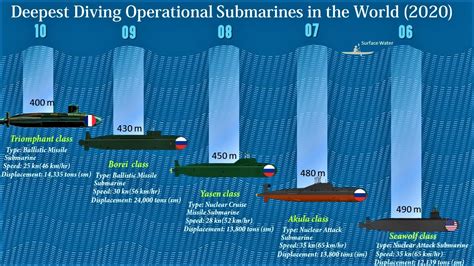
There are several types of submarines, each with its own unique characteristics and depth capabilities. These include: * Conventional submarines: These submarines use diesel-electric propulsion and have a limited depth capability, typically around 200-300 meters. * Nuclear submarines: These submarines use nuclear reactors for propulsion and have a much greater depth capability, typically around 400-500 meters. * Deep-diving submarines: These submarines are designed for deep-sea exploration and can dive to depths of over 1,000 meters. * Special-purpose submarines: These submarines are designed for specific tasks, such as underwater construction or research, and may have unique depth capabilities.
Depth Records

The deepest dive ever recorded by a submarine was made by the Bathyscaphe Trieste in 1960, which reached a depth of 10,973 meters in the Mariana Trench. However, this was a specialized deep-diving submersible, not a conventional submarine. The deepest dive by a conventional submarine was made by the USS Triton in 1960, which reached a depth of 682 meters.
Table of Submarine Depth Capabilities
| Submarine Type | Depth Capability |
|---|---|
| Conventional submarine | 200-300 meters |
| Nuclear submarine | 400-500 meters |
| Deep-diving submarine | 1,000-2,000 meters |
| Special-purpose submarine | variable |

🚨 Note: The depth capabilities listed in the table are approximate and can vary depending on the specific submarine and its design.
Challenges of Deep-Sea Exploration

Deep-sea exploration is a challenging and complex task, requiring specialized equipment and trained personnel. Some of the challenges of deep-sea exploration include: * Pressure: The pressure at great depths is extreme, reaching over 1,000 times the pressure at sea level. * Temperature: The temperature at great depths is near-freezing, ranging from just above 0°C to 4°C. * Corrosion: The seawater is corrosive, and the submarine’s hull and equipment must be designed to withstand it. * Communication: Communication with the surface is difficult at great depths, and submarines must use specialized equipment to stay in touch.
Future of Submarine Depth Exploration
The future of submarine depth exploration is exciting and rapidly evolving. New technologies, such as advanced materials and propulsion systems, are being developed to enable submarines to dive deeper and stay underwater longer. Additionally, the use of autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) and remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) is becoming increasingly common, allowing for greater flexibility and efficiency in deep-sea exploration.
In summary, submarine depth is a complex and fascinating topic, influenced by a combination of factors including hull design, materials, ballast tanks, life support systems, and pressure hull. Different types of submarines have varying depth capabilities, and deep-sea exploration is a challenging and complex task. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see new and exciting developments in the field of submarine depth exploration.
What is the deepest dive ever recorded by a submarine?

+
The deepest dive ever recorded by a submarine was made by the Bathyscaphe Trieste in 1960, which reached a depth of 10,973 meters in the Mariana Trench.
What is the difference between a conventional submarine and a nuclear submarine?

+
A conventional submarine uses diesel-electric propulsion, while a nuclear submarine uses a nuclear reactor for propulsion. Nuclear submarines have a much greater depth capability and can stay underwater for longer periods.
What are the challenges of deep-sea exploration?
+
The challenges of deep-sea exploration include extreme pressure, near-freezing temperatures, corrosion, and communication difficulties. Submarines must be designed to withstand these conditions, and specialized equipment is required to stay in touch with the surface.
Related Terms:
- Submarine depth chart
- Deepest submarine dive
- maximum depth of nuclear submarine
- how deep can submersibles go
- us navy submarine maximum depth
- deepest diving nuclear submarine