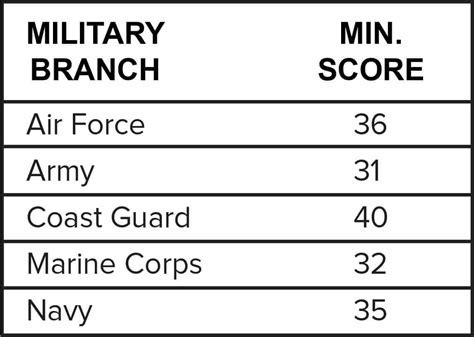
5 Key Healthcare Agencies
Introduction to Healthcare Agencies

The healthcare system is complex and multifaceted, involving various agencies that play crucial roles in ensuring the delivery of high-quality patient care, promoting public health, and regulating the industry. These agencies operate at different levels, from local to international, and their responsibilities can range from disease control and prevention to setting standards for healthcare practices. Understanding the functions and contributions of these agencies is essential for navigating the healthcare landscape effectively.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)

The CDC is a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services. It is one of the major operating components of the Department of Health and Human Services. The CDC’s mission is to protect America from health, safety, and security threats, both foreign and in the U.S. Whether diseases start at home or abroad, are chronic or acute, curable or preventable, human error, deliberate attack, or climate change, the CDC is committed to protecting the American people. The agency focuses on infectious and environmental diseases, foodborne pathogens, and injury control among other areas. The CDC also provides critical funding and technical assistance to state and local health departments.
World Health Organization (WHO)

The WHO is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, and was established in 1948. The main objective of the WHO is “the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of health”. This organization plays a critical role in global health matters, especially on issues such as influenza pandemics, mental health, and drug resistance. The WHO also promotes healthcare access and standards worldwide, striving to make the world a healthier place.
National Institutes of Health (NIH)

The NIH, a part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, is the nation’s medical research agency. It is composed of 27 Institutes and Centers, each with a specific research agenda focusing on particular diseases or body systems. The NIH’s mission is to seek fundamental knowledge about the nature and behavior of living systems and to apply that knowledge to enhance health, lengthen life, and reduce the burdens of illness and disability. This agency supports research and innovation in the field of medicine, making it a pivotal player in advancing healthcare.
Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
The FDA is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting the public health by ensuring the safety, efficacy, and security of human and veterinary drugs, biological products, and medical devices. The agency also regulates food, cosmetics, radiation-emitting products, and tobacco products. The FDA plays a critical role in regulating and monitoring the healthcare industry, ensuring that products are safe for public use.
European Medicines Agency (EMA)

The EMA is a European Union agency responsible for the evaluation and supervision of medicinal products for both human and veterinary use. It began operating in 1995 as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products (EMEA), and was renamed in 2009. The agency is located in Amsterdam, Netherlands. The EMA’s main responsibility is to coordinate the evaluation and monitoring of medicines developed by pharmaceutical companies for use in the European Union. This includes ensuring that medicines are safe, effective, and of high quality.
📝 Note: These agencies work closely together and with other organizations to ensure the highest standards of public health and safety are maintained.
In reviewing the functions of these critical healthcare agencies, it becomes clear that their roles are multifaceted and interconnected. From research and development to regulation and public health initiatives, these organizations are essential in advancing healthcare globally. Understanding their contributions can provide valuable insights into the complexities of the healthcare system and the importance of collaborative efforts in improving health outcomes.
What is the primary role of the CDC?

+
The primary role of the CDC is to protect America from health, safety, and security threats, both foreign and in the U.S., through disease control and prevention, and promoting public health.
How does the WHO contribute to global health?
+
The WHO contributes to global health by setting global standards, providing critical funding and technical assistance, and coordinating international responses to health crises.
What is the mission of the NIH?

+
The mission of the NIH is to seek fundamental knowledge about the nature and behavior of living systems and to apply that knowledge to enhance health, lengthen life, and reduce the burdens of illness and disability.
Related Terms:
- Regulatory abbreviation
- Pharmaceutical industry abbreviations PDF
- Regulatory Rapporteur
- PIL regulatory affairs
- Pharma abbreviations
- Topra regulatory intelligence