5 Ways Universal Healthcare Works

Introduction to Universal Healthcare

Universal healthcare is a system in which all residents of a country have access to medical services without facing financial hardship. The goal of universal healthcare is to provide comprehensive, high-quality healthcare to everyone, regardless of their income, social status, or health condition. In this post, we will explore five ways universal healthcare works and its benefits.
How Universal Healthcare Systems Are Funded
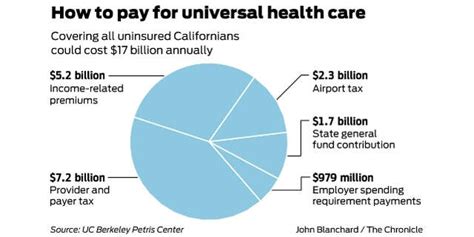
Universal healthcare systems are typically funded through a combination of methods, including taxes, premiums, and out-of-pocket payments. The funding model may vary depending on the country and its healthcare system. For example, some countries like the United Kingdom and Canada have a single-payer system, where the government is the primary payer for healthcare services. In contrast, countries like Germany and France have a multi-payer system, where both the government and private insurance companies play a role in funding healthcare.
Key Components of Universal Healthcare Systems

There are several key components of universal healthcare systems, including: * Comprehensive coverage: Universal healthcare systems provide comprehensive coverage for a wide range of medical services, including doctor visits, hospital stays, surgeries, and prescription medications. * Accessibility: Universal healthcare systems aim to make healthcare services accessible to everyone, regardless of their income or social status. * Quality of care: Universal healthcare systems strive to provide high-quality care to all patients, regardless of their background or health condition. * Preventive care: Universal healthcare systems often emphasize preventive care, such as routine check-ups, screenings, and vaccinations, to prevent illnesses and promote health.
Benefits of Universal Healthcare

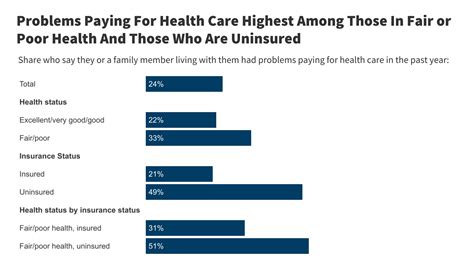
The benefits of universal healthcare are numerous, including: * Improved health outcomes: Universal healthcare systems have been shown to improve health outcomes, particularly for vulnerable populations such as the poor and the elderly. * Reduced healthcare costs: Universal healthcare systems can help reduce healthcare costs by eliminating administrative costs and negotiating lower prices with healthcare providers. * Increased access to care: Universal healthcare systems can increase access to care, particularly for those who were previously uninsured or underinsured. * Reduced financial burden: Universal healthcare systems can reduce the financial burden of healthcare costs on individuals and families.
Examples of Successful Universal Healthcare Systems

There are many examples of successful universal healthcare systems around the world, including: * Taiwan: Taiwan’s universal healthcare system, known as the National Health Insurance (NHI) system, provides comprehensive coverage to all citizens and has been shown to improve health outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. * Japan: Japan’s universal healthcare system, known as the Universal Health Insurance (UHI) system, provides comprehensive coverage to all citizens and has been shown to improve health outcomes and increase access to care. * Sweden: Sweden’s universal healthcare system, known as the Swedish Health Insurance system, provides comprehensive coverage to all citizens and has been shown to improve health outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
👍 Note: These examples are just a few among many successful universal healthcare systems around the world.
Challenges and Limitations of Universal Healthcare
While universal healthcare systems have many benefits, they also face several challenges and limitations, including: * High costs: Universal healthcare systems can be expensive to implement and maintain, particularly in countries with limited resources. * Long wait times: Universal healthcare systems can experience long wait times for non-emergency procedures, particularly in countries with limited healthcare resources. * Quality of care: Universal healthcare systems can struggle to provide high-quality care, particularly in countries with limited healthcare resources.
| Country | Universal Healthcare System | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Taiwan | National Health Insurance (NHI) system | Comprehensive coverage, single-payer system |
| Japan | Universal Health Insurance (UHI) system | Comprehensive coverage, multi-payer system |
| Sweden | Swedish Health Insurance system | Comprehensive coverage, single-payer system |

In summary, universal healthcare systems provide comprehensive coverage to all residents of a country, regardless of their income or social status. These systems have many benefits, including improved health outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, and increased access to care. However, they also face several challenges and limitations, including high costs, long wait times, and quality of care issues. By understanding how universal healthcare systems work and their benefits and challenges, we can work towards creating a more equitable and effective healthcare system for all.
What is universal healthcare?
+
Universal healthcare is a system in which all residents of a country have access to medical services without facing financial hardship.
How are universal healthcare systems funded?

+
Universal healthcare systems are typically funded through a combination of methods, including taxes, premiums, and out-of-pocket payments.
What are the benefits of universal healthcare?
+
The benefits of universal healthcare include improved health outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, increased access to care, and reduced financial burden on individuals and families.