Cyber Operations Explained
Introduction to Cyber Operations
Cyber operations are a crucial aspect of modern warfare and national security. They involve the use of computer networks and systems to disrupt, disable, or destroy an adversary’s ability to operate. Cyber attacks can be launched against a wide range of targets, including military command and control systems, critical infrastructure, and civilian populations. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of cyber operations, exploring their history, types, and implications for national security.
History of Cyber Operations
The concept of cyber operations dates back to the 1970s, when the United States and the Soviet Union first began exploring the potential of computer networks for military purposes. However, it wasn’t until the 1990s that cyber operations began to take shape as a distinct domain of warfare. The US Department of Defense established the first cyber warfare unit in 1995, and since then, other countries have followed suit. Today, cyber operations are an integral part of military strategy, with many countries investing heavily in their cyber capabilities.
Types of Cyber Operations
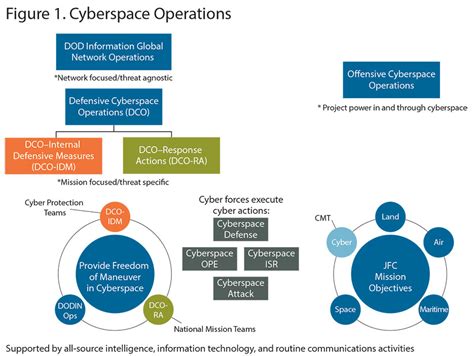
There are several types of cyber operations, including: * Cyber attacks: These involve the use of malware, viruses, or other types of malicious software to disrupt or destroy an adversary’s computer systems. * Cyber espionage: This involves the use of cyber operations to gather intelligence on an adversary’s military capabilities, strategic plans, or other sensitive information. * Cyber defense: This involves the use of cyber operations to protect one’s own computer systems and networks from cyber attacks. * Cyber support: This involves the use of cyber operations to support military operations, such as by providing intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities.
Cyber Operations and National Security
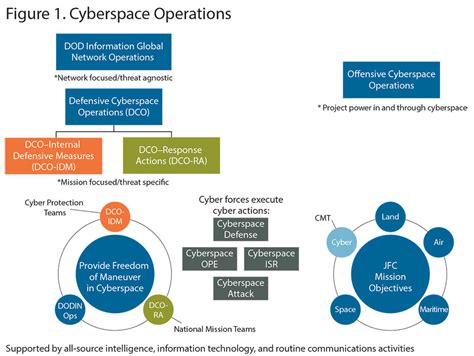
Cyber operations have significant implications for national security. Cyber attacks can be used to disrupt critical infrastructure, such as power grids, financial systems, and transportation networks. They can also be used to steal sensitive information, such as military secrets or personal data. Furthermore, cyber operations can be used to influence public opinion, spread propaganda, and undermine democratic institutions. As such, it is essential for countries to develop robust cyber defenses and to invest in cyber operations capabilities to protect their national security.
Cyber Operations and International Law

The use of cyber operations raises important questions about international law. International humanitarian law (IHL) applies to cyber operations, just as it does to traditional kinetic warfare. This means that cyber attacks must distinguish between military targets and civilian objects, and must avoid causing unnecessary harm to civilians. Additionally, cyber operations must comply with the principles of necessity and proportionality, which require that the use of force be necessary and proportionate to the military objective.
| Type of Cyber Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Cyber Attack | The use of malware, viruses, or other types of malicious software to disrupt or destroy an adversary's computer systems. |
| Cyber Espionage | The use of cyber operations to gather intelligence on an adversary's military capabilities, strategic plans, or other sensitive information. |
| Cyber Defense | The use of cyber operations to protect one's own computer systems and networks from cyber attacks. |
| Cyber Support | The use of cyber operations to support military operations, such as by providing intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities. |

💡 Note: The use of cyber operations raises important questions about international law, including the application of international humanitarian law (IHL) and the principles of necessity and proportionality.
Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, cyber operations are a critical aspect of modern warfare and national security. They involve the use of computer networks and systems to disrupt, disable, or destroy an adversary’s ability to operate. As the use of cyber operations continues to evolve, it is essential for countries to develop robust cyber defenses and to invest in cyber operations capabilities to protect their national security. Furthermore, the international community must work together to develop norms and standards for the use of cyber operations, and to ensure that they are used in a way that is consistent with international law.
What is the difference between a cyber attack and cyber espionage?

+
A cyber attack involves the use of malware, viruses, or other types of malicious software to disrupt or destroy an adversary’s computer systems, while cyber espionage involves the use of cyber operations to gather intelligence on an adversary’s military capabilities, strategic plans, or other sensitive information.
What are the implications of cyber operations for national security?

+
Cyber operations have significant implications for national security, including the potential to disrupt critical infrastructure, steal sensitive information, and influence public opinion. As such, it is essential for countries to develop robust cyber defenses and to invest in cyber operations capabilities to protect their national security.
What is the role of international law in regulating the use of cyber operations?

+
International law, including international humanitarian law (IHL), applies to cyber operations, just as it does to traditional kinetic warfare. This means that cyber attacks must distinguish between military targets and civilian objects, and must avoid causing unnecessary harm to civilians. Additionally, cyber operations must comply with the principles of necessity and proportionality, which require that the use of force be necessary and proportionate to the military objective.
Related Terms:
- cyber operations vs security
- cyber operations examples
- types of cyberspace operations
- definition of cyber operations
- military cyber operations
- dod cyberspace operations



